Aggression is the most serious dog behavior problem any owner may encounter. Once a dog displays excessive aggression, the problem becomes very difficult to remedy, even for seasoned professional trainers. That is why it is vital for owners to understand the major causes and types of aggression in order to prevent their K-9s from developing dangerous behavioral problems.
Causes
Genetic and hereditary factors play a major role in aggression. Working breeds such as Dobermans, German Shepherds, and Rottweilers are expected to be more aggressive than Golden Retrievers and Labradors, for example. However, even in the most aggressive lines, a responsible breeder will know how to influence the genetic variables that control aggression. Only novice or unscrupulous breeders will promote aggressive characteristics in the breeding process, confusing these dangerous qualities for the traits sought after in guard dogs.
Another genetic factor, excessive inbreeding, may also result in an aggressive dog. In Egypt, owners should be wary of local breeders, as due to the limited K-9 lines available, breeders tend to inbreed their dogs. The upshot is pups with unstable temperaments, so that the dogs often become either too aggressive or extremely timid.
In addition to genetic factors, environmental circumstances profoundly affect K-9 behavior. Lack of socialization, isolation from human contact, excessive punishment or teasing, or even excessive praise or leniency by owners can all contribute to creating an aggressive dog. Although most owners understand that harsh treatment creates K-9 behavioral disorders, many do not understand that being too lenient may do the same.
Dogs have a pack order that determines their social rank. They see the humans they live with as members of their pack, and they try to establish their rank while determining yours. This means that your dog may try to establish an alpha position by challenging the more submissive family members, like children. Therefore, it is vital that owners correct any dominance displays by their dogs as soon as they begin. Such displays include resisting known commands, growling at family members, and aggressively guarding their food. Owners need to be aware that aggressive behavior is a progression; so if the initial attempts at dominance are not corrected, the problem will escalate, and the dog may end up biting someone.
Types of Aggression
There are several types of aggression: defensive, dominant, possessive, territorial, predatorial or parental. The two major distinctions of aggression are dominant-aggressive and defensive-aggressive with dogs displaying the other characteristics within these classifications. A dog may exhibit one or more types of aggression at a time, in different situations, depending on the environmental stimulant.
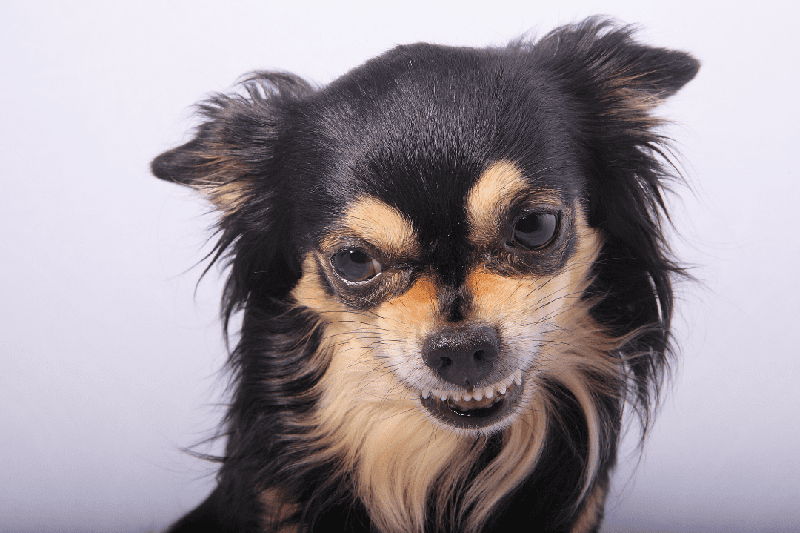
Dominant-aggressive dogs are confident, macho alpha males. They stand tall, their ears are up and forward, and they carry their tails high and wag them slowly, stiffly from side to side. These dogs demand attention and excessive affection. Many of these dogs will not obey commands, especially submissive commands, such as“down.” If you encounter one of these types, do not challenge him and avoid any direct eye contact. These dominant K-9s will rise to the challenge and be at you before you know it.
Defensive-aggressive dogs are triggered by fear, pain, or fear of punishment. They display submissive body language such as ears back and flat against the head, avoidance of direct eye contact, lowering of the head and body, tucking the tail between the legs, submissive urination, hand licking and rolling over to expose their bellies. They resist handling, hate to have their feet touched, don’t like to be groomed and often shy away from human hands. These are the fear-biters; they may snap if cornered and may bite at people who turn and walk away.
Preventing aggression
To begin with, always make sure you deal with a reputable breeder when getting a dog. There are many unknowns when choosing a puppy, but at least with an ethical breeder there are fewer unwanted surprises–including innate aggression. Once your puppy is at home, train him properly with firmness and kindness. Never allow your pup or dog to achieve dominant status over any child or adult by immediately correcting any attempts he makes. Be consistent so your dog always knows his social rank and does not try to challenge people. In this way he is sure to become your best friend and a loved and lovable member of your family.
How to Avoid Dog Attacks
- Dot not run when confronted by an aggressive dog. Running only stimulates the dog to increase its aggression.
- Hold your ground and demonstrate moderate dominance by firmly telling the dog, “No!” This usually works wonders.
- Avoid direct eye contact, which the dog interprets as a challenge. Instead, appear nonchalant.
- When the dog begins to back away, you should retreat as well. Keep the dog in view, but don’t give it any direct attention.
- If the dog begins to come back, stop and wait until it moves off again.
- As a last resort, throw or pretend to throw an object at an aggressive dog.
- If attacked, feed the dog your jacket, bike, purse, book or anything you have to distract it from your body.